Week 7 subject 1: Classes
- 'Objects' are grouped into Classes. Classes define the common properties and capabilities of objects. Objects are 'instances' of their respective Classes. Example: 'Cars' is a Class, and my 2020 BMW 320i is an object of this Class, my friend's 2018 Honda CRV is another object of this Class.
- Instances of Classes are accessed in Python by declaring variables of a Class (objects). A Class is essentially a type, like int or string.
- Just like there are different levels of group objects in real life, there can be hierarchies of Class definitions. Objects can be instances of different Classes.
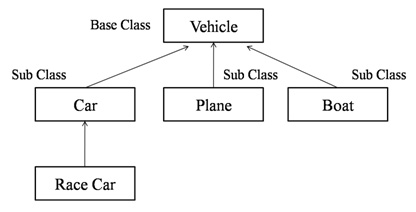
- Parent Classes / Child Classes; Base Classes / Sub Classes.
- There's inheritance between parent and child classes.
- Define Classes, use pass to indicate you don't define the contents of the Class at this moment;
Class Car:
pass
Class Car(Vehicle):
define drive():
pass
define park():
pass
- You can define variables and functions inside Classes. Variables are called Attributes, functions are called Methods of Classes.
- Note: because of inheritance, instances of child classes can access members of parent classes.
Week 7 subject 2: Attributes
- Attributes of Classes are created when they are assigned values.
- Attributes can be dynamically added or deleted (with del statement).
- Parent and child Classes can have Attributes with the same names, when referred to, child will override parent.
- ADVANCED: Attributes can be attached to the Class as well as the Instance. In the former they are called Class Attributes, latter Instance Attributes. Class Variable values are common across all instances of the Class, while Instance Attributes values are local to the exact instance.
class Car(vehicle):NumOfWheels = 4
def move(self, direction, distance):
pass
myCar.NumOfWheels = 5
print(Car.NumOfWheels, myCar.NumOfWheels)
myCar = Car()
Week 7 subject 3: Methods
- Methods are functions attached to Classes. Like functions they need to be defined before being used.
- Methods have 1 implicit parameter: self. self means the Instance itself. methods use the self variable to access other members of the Instance.
class Car(vehicle):
NumOfWheels = 4
def move(self, direction, distance):
pass
def showwheels(self):
print(self.NumOfWheels)
- Like Attributes, parent and child classes can define methods with the same names. When called, child will override parent.
- ADVANCED: Methods can also be added to Classes after initial definition of Classes. Methods can be attached to both the Class and the Instance. This is too complex, don't try.
Week 7 subject 4: Python built-in functions
- abs(x): find out absolute values
- bool(x): returns truth value
- dir(object): returns all information(attributes) of the object
- help(request): evoke the online help system
- eval(expression): run and return result
- exec(object): run expression or program(!)
- float():
- int():
- len():
- min() and max():
- range():
- sum():
constants defined to be false:
NoneandFalsezero of any numeric type:
0,0.0,0j,Decimal(0),Fraction(0, 1)empty sequences and collections:
'',(),[],{},set(),range(0)
No comments:
Post a Comment